Cloud Computing: What is it and what are its advantages?

Cloud Computing is an online storage service that allows users to access computing resources, such as online storage, processing, and software, over the internet, instead of relying on their own physical system. It's like renting computing capacity instead of buying and maintaining your own infrastructure.
Currently, developing an application involves dealing with a large amount of information, which in many cases can be costly from implementation to maintaining servers. All this added to various limitations such as the inability of remote use or lack of constant updating.
A viable solution to this problem is cloud computing, however, it may not be the best option for all companies, as some may simply find it unuseful according to their policies or activities. But for many others, it was a great revolution that helped to optimize the way things were done, reduce costs, and achieve constant stability on virtual platforms that are so widely used today.
Cloud computing emerged as an alternative to the traditional system, as maintaining a server that supports a website or mobile applications is time-consuming, requires qualified personnel, and can be very costly.
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud Computing refers to the delivery of computing services and resources over the internet. Thanks to this technology, it's no longer necessary to own and manage data servers and storage on-site; instead, you can now leverage these computing resources through cloud service providers. These resources include virtual servers, storage, databases, software, and more, paying only for what you use.
Some of the key features of Cloud Computing are:
Network Access: Cloud computing services and resources are offered and utilized over a network, typically the Internet. This means that users can access their applications, data, and content from anywhere in the world, at any time, as long as they have an Internet connection.
On-Demand Self-Service: IT teams can provision computing resources, such as server time and network storage, as needed automatically, without requiring human intervention from the service provider.
Scalability and Elasticity: Resources can be scaled up or down quickly and, in some cases, automatically, to adjust to demand, allowing for great flexibility and optimization of resources.
Pay-Per-Use Model: Computing resources are measured at a fine-grained level, enabling users to pay only for the resources and services they actually use.
Measured Services: The use of resources can be controlled, measured, and reported, providing transparency for both the provider and the user of the consumed service.
Automatic Maintenance and Updates: Software and platforms are updated automatically, ensuring users access to the latest versions and technologies without additional maintenance effort.
Device Location Independence: Users can access cloud computing services regardless of their location or the device they are using, be it a computer, a mobile phone, or a tablet.
Types of Cloud Computing Deployments
There are several types of Cloud Computing deployments used to provide cloud computing services. These deployments differ in how computing resources are configured and managed. The three main types of deployments are:
Public Clouds: This type of cloud allows renting digital space online offered by cloud service providers that are owned and operated by companies. The main advantage is that you can obtain computing, storage, and network resources over the internet, which allows businesses to access shared resources according to their unique requirements and business goals.
Private Clouds: This approach provides a secure online space where data and applications are stored on servers that are owned and exclusively controlled by the company. The main advantage of this cloud is that it offers more control, security, and data management, allowing users to benefit from these resources.
Hybrid Clouds: This is a combination of both types of clouds. It offers the advantage of being able to store data and applications on private servers for greater security, while public servers can be used for greater flexibility and savings.
Cloud Computing Service Models
There are different categories to better understand cloud computing, however, there are 3 main ones:
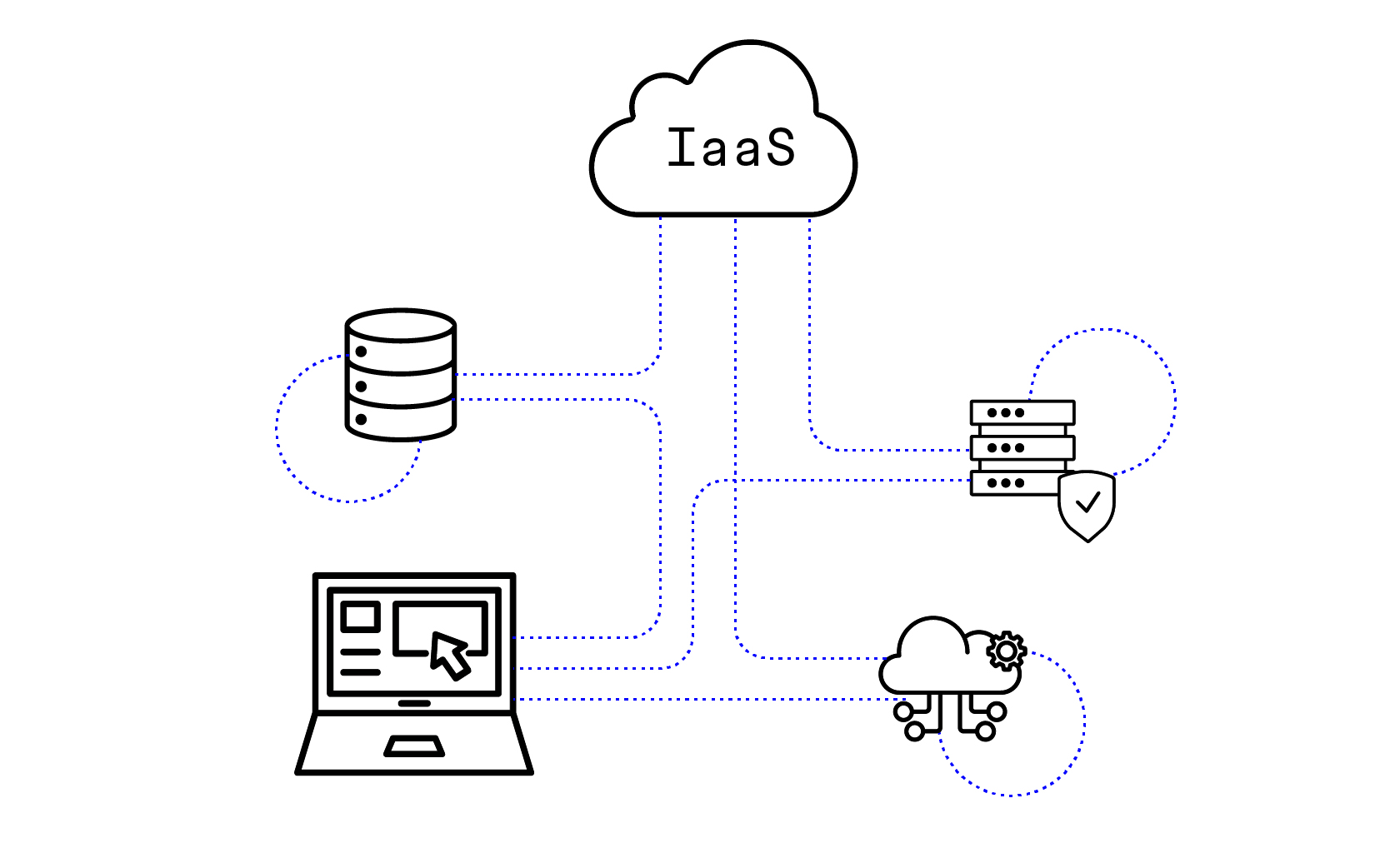
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): In this stage, it is possible to rent a network of servers in the cloud and storage; thus eliminating the need to buy and maintain costly physical hardware, saving time and money.
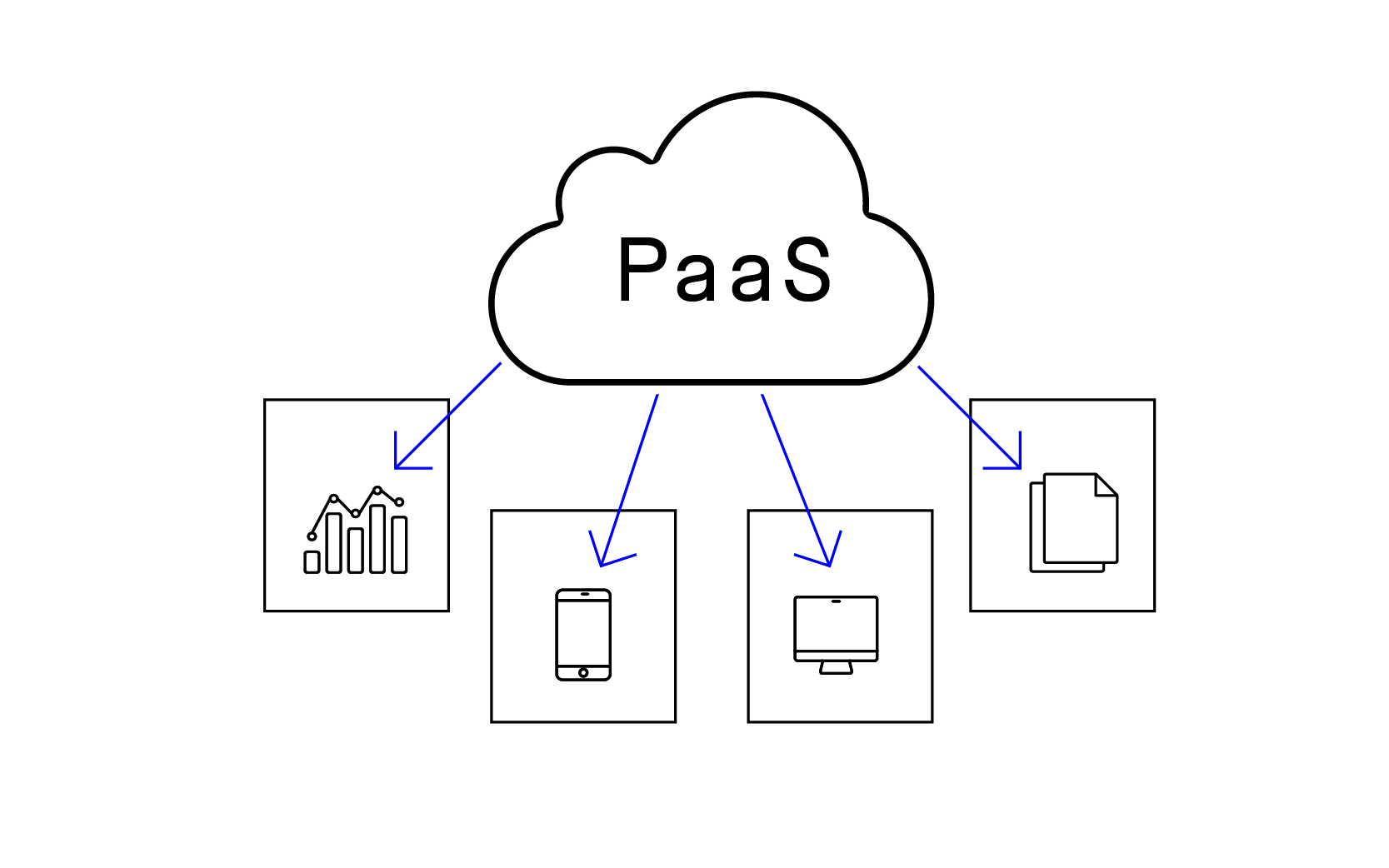
Platform as a Service (PaaS): In this category, a complete development platform in the cloud is provided. Developers can create, test, and deploy applications without worrying about the infrastructure.
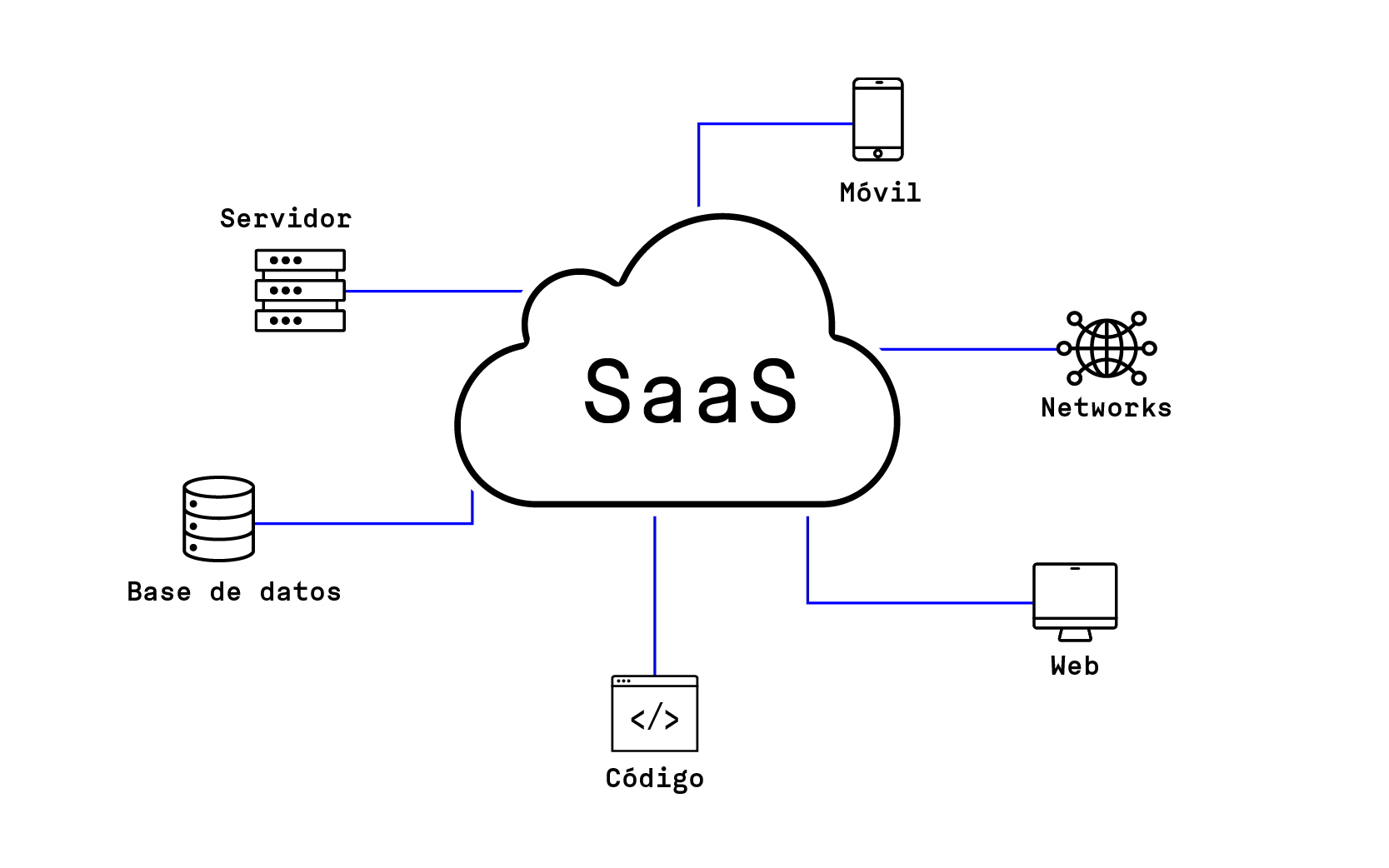
Software as a Service (SaaS): In this top layer, it will be possible to access applications and software through the cloud, including productivity suites and business applications.
Advantages of Cloud Computing
Scalability: Resources can be easily adjusted according to demand, allowing businesses to expand or reduce their services quickly and efficiently.
Cost Efficiency: By using cloud services, the need to invest in hardware, maintenance, and upgrades is reduced. You only pay for the resources you use.
Accessibility: Users can access services and data from anywhere in the world, as long as they have an internet connection.
Flexibility: The cloud offers a wide range of applications and services, allowing businesses to select the options that best suit their needs.
Disaster Recovery: Many cloud service providers offer data backup and recovery solutions, minimizing the loss of information in case of failures or disasters.
Automatic Updates: Cloud services are automatically updated and maintained, freeing businesses from the concern of software and hardware updates.
Security: Although security remains a concern, many service providers offer secure cloud storage through various robust security measures to protect client data and applications.
Enhanced Collaboration: With data and applications accessible online, teams can collaborate more easily, as they can access, edit, and share information in real time from anywhere.
Speed in Deployment: Cloud services can be deployed quickly, allowing businesses to get their applications and services up and running in less time compared to owning a physical infrastructure.
Lower Environmental Impact: By sharing resources in a cloud environment, energy use is optimized, which can result in a smaller carbon footprint.
Disadvantages of Cloud Computing
Vendor Dependence: The company may become too dependent on a cloud service provider.
Security and Privacy: Although many providers offer robust security measures, managing sensitive data in the cloud can present risks.
Availability and Downtime: Dependence on cloud services can be problematic if the provider experiences service interruptions.
Limitations on Customization and Control: There may be restrictions on the ability to customize and control certain aspects of the service.
Unexpected Costs: If not managed properly, costs associated with using cloud services can unexpectedly increase.
Compliance and Legal Issues: Some sectors or regions may have regulations that limit or complicate the transfer and storage of data in the cloud.
Bandwidth: Costs may increase or access speed may be limited if the bandwidth limit set by the provider is exceeded.
In summary, Cloud Computing has revolutionized the way businesses manage their technological operations. It offers flexibility, efficiency, and cost savings, making it an extremely useful and essential tool in today's business world. As technology continues to advance, Cloud Computing will continue to play a fundamental role in the digital transformation of organizations.


